A research lab in an institute or university gets funds for research from many public and private funding agencies. The National Institute of Health (NIH) is one of the major government funding agencies. It supports 84% of biomedical research in academia, small institutes, and small businesses (source: researchamerica.org). In 2024, NIH invested $47.1 billion in research. For every $1 invested in NIH-funded research, $2.46 is generated in economic activity.
For clinical trials, most of the funding comes from the pharmaceutical industry. 63.9% of clinical trials are industry sponsored. Oncology is the top therapeutic area for clinical trials, comprising 30.5% of clinical trials (Figure 1). The top 5 disease areas in which the clinical trials are focused are oncology, CNS, infectious disease, metabolic disease, and gastrointestinal disease. Most of the trials are in phase 2 (Figure 2).
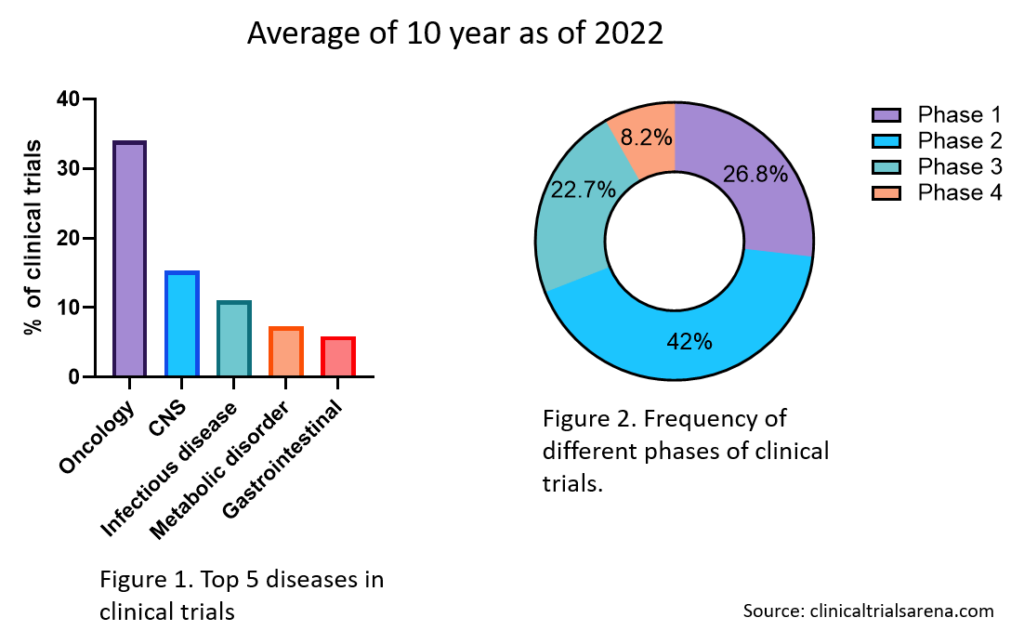
Overall, it costs around USD 2 billion to bring a drug to market from discovery to launch. The success rate of clinical trials is only 7.9%. With such a high price, and low success rate, drug discovery is a high-risk high-reward project. Thus, better methods are required to test these drugs pre-clinically, to increase the success rate in clinical trials.