
What is biomedical research?
Issac Newton famously said “If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of Giants” which perfectly sums up the research process. The process involves stepwise determination of a problem, finding what is known till now, and using that knowledge to determine its solution. Biomedical research focuses on developing new drugs or devices to improve human health by treating diseases or delaying their progression. There are mainly three kinds of research – basic, translational, and clinical.
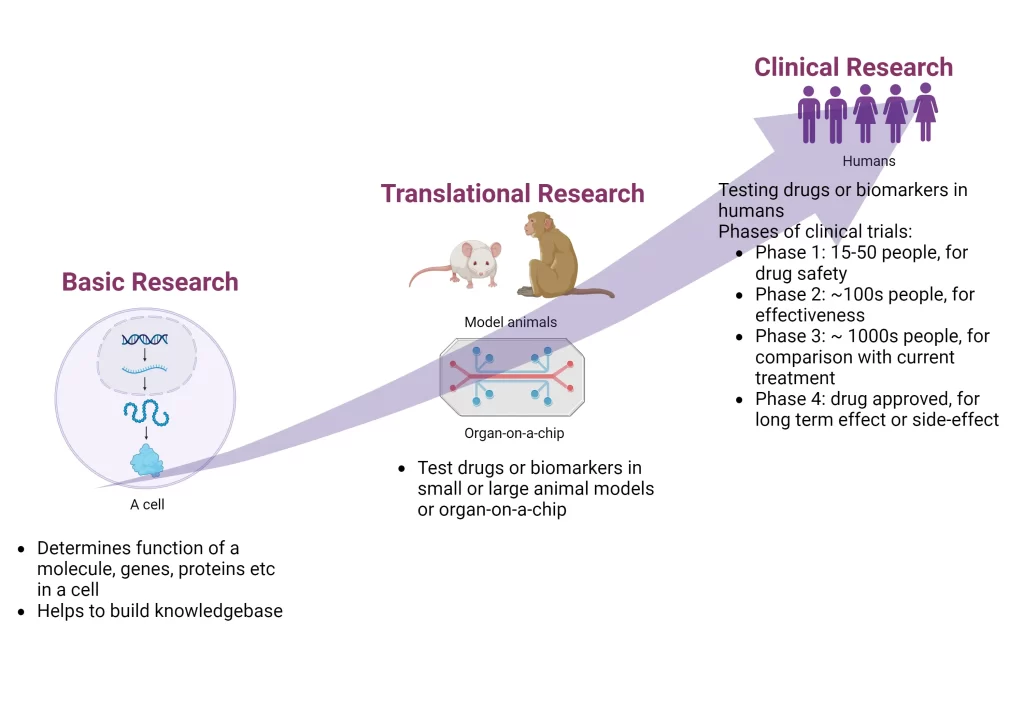
Basic research focuses on building the knowledge base, which forms the basis for finding drugs or techniques. A few examples include discovering new genes/proteins and finding their function. Developing new techniques that make the research process more efficient such as high-throughput data generation and analysis.
Translational research focuses on drugs, diagnostics, or devices that have clinical applications. Drug discovery includes drugs to treat a disease. Diagnostics include biomarkers discovery to find if a person has a disease or determine its severity. Devices include any instrument, machine, implant, etc that can be used for medical purposes and support human health. The candidate drugs, biomarkers, or biomarkers are tested in small and large animals in a lab before testing in humans. This is also called pre-clinical research.
Clinical research involves testing potential drugs, biomarkers, or devices in humans called clinical trials. All these kinds of research are important in moving healthcare research and development forward. However, clinical trials are most time and resource consuming.
